| Geophysical sounding for ore deposit exploration | 39 locations |
| Extraction of oil | 21 locations |
| Extraction of natural gas | 1 location |
| Construction of inground gas reservoir | 35 locations |
| Construction water reservoir for drinking | NA |
|
Figure 1 Distribution map of underground nuclear explosions in the Soviet Union |
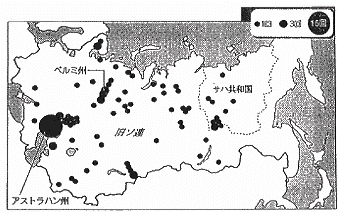 |
|
Figure 2 Distribution map of major nuclear explosions in Kazakhstan |
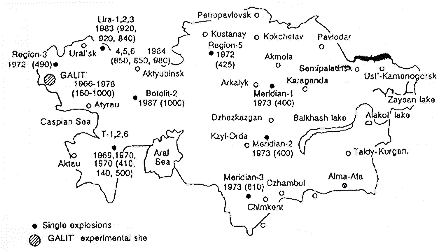 |
- Recently some people who were responsible to the underground nuclear explosion in Sakha published their reports on the tests and possible hazards caused by contamination (Chomchoev et al. 1994, Mikulenko et al. 1996). The present author had the chance to discuss with these people during a stay in Yakutsk. In addition to this information, he visited some remote locations along the Arctic coast. These experiences induced the present situation of radioactive contamination in the arctic regions of Siberia. After 1988 under the movement of Glasnost, some people who were connected with carrying out the test dared to disclose the fact of the explosion. Some of these people are fully responsible for the nuclear explosion, and afterward for the accident at the nuclear power plant in Chernobyl. They simply confessed their act would be guilty for future generations.
Figure 3
Distribution map of underground nuclear explosions in Sakha
(note: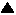 mark indicates the site of nuclear missile accidents)
mark indicates the site of nuclear missile accidents)
- According to the report by Chomchoev et al. (1994), between 1967 and 1988, the total number of the explosions was 12. The nearest site is located at Kobyai, and is 70 km away from city of Yakutsk. On the 8th August 1978, the explosion, code named "Craton-4", was carried out at a depth of 567 m in the previously arranged bore hole. The size of the explosion was equivalent to 6.15 kt of dynamite. In that area there is a tectonic zone and a fault zone, runing from south-west to north-east. The geological setting of the Carton-4 site suggests that migration of underground water may spread out along the tectonic zone. They predicted the possible flow of contaminated water shown in Fig. 4. The most hazardous pollutant is 239plutonium, which has a half life time of about 28,000 years.
Figure 4
Possible flow of radioactive contaminated water from Craton-4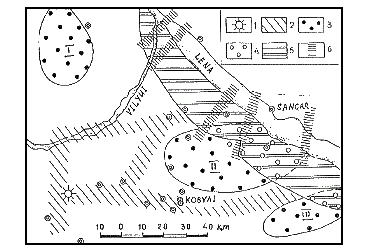
- : epicenter of explosion
- : contamination along faults
- : underground accumulation of pollutant in syncline zone
- : accumulation on the river bed
- : accumulation at the thrust zone
- : possible site of infiltration of pollutant to dry surface
- The other site, where severe contamination after the explosion occurred is Udachnyi in 440km away from Mirnyi. This area is a major site of diamond mining industries operation. The explosion was carried out in 1992 with the code name "Crystal". Instead of being a geophysical sounding like Craton-4, Crystal was designed to build up a rock-fill dam. It is necessary to treat water from diamond industries because of the high concentration of heavy metal in the discharged water. Alter contaminated water is poured into the water reservoir, the suspended material may settle down after a certain time period. In the early 1980s near Udachnyi along the stream there are rather steep slopes, and nuclear explosives were set in the bedrock on the slope at a depth of 100m or less. The depth of the epicenter was too shallow to prevent the leakage of contaminated pollutants to the ground surface. The main objective of this explosion was to trigger the land slide from the steep slope. The designed gravel fill for this dam was 75m in height and it is estimated that enough gravel was created by the explosion. It was revealed that some amounts of 137Cs, 90Sr and 239plutonium were emitted in the explosion. The size of the nuclear explosive was the equivalent of 20-25kt of conventional explosive. After the explosion, the height of piled gravel was less than 13m and was not enough for the initial purpose as a water reservoir. The contaminated area was covered by concrete to stop further dispersion of the pollutant. But 1981, a preliminary survey at the site was conducted and a high level of radiation of gamma ray of Cs was traced. In addition to the gamma ray source, 239plutonium and 240plutonium were found in the soil and lichen with values 5 to 6 times higher than the safety standard. Drugs of Caribou also contained highly concentrated 239plutonium. There will be a serious concern of the wide dispersion of plutonium into the ecosystem in the area adjacent to Crystal. Potential danger of cancer among the local people will be warned in future. No action has yet been taken by either local or federal governments.
- The US government paid a great deal of attention to the situation in the Arctic Sea caused by radioactive contamination. The task force program was organized by Naval Research office and the annual report was published in 1996. One of the byproducts from nuclear waste is 237Neptunium and samples from Yenisei and Ob were analyzed for concentrations of it. The results of measurements were compared with other sediments obtained in arctic Canada and the trans-Arctic ocean (see Table 1).
Table 1
Concentration of 237Neptunium (Naval Research Office 1996)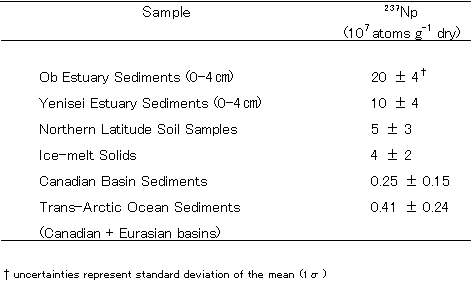
- The estimated source of 237Neptunium is during the processing of nuclear power plant fuel. As in the middle stream of Yenisei near Krasnoyarsk region, the plant for processing and reprocessing nuclear bombs used to be active under the code name "Krasnoyarsk 26", In the early 1960s a serious accident occurred at Krasnoyarsk 26. A high amount of pollutant was discharged into the Yenisei River. Most of the pollutants, such as plutonium, settled on the river bed due to their high density. However, in 1968, heavy flooding of the river washed away the sedimented pollutant and dispersed it widely in the down stream region. One of the local authorities at Krasnoyarsk pointed out the pollutant will migrate to the mouth of Yenisei 500km away. Many local cities and towns along the river, located lower than the Krasnoyarsk use river water for drinking. In 1992 two nuclear plants for the production of nuclear bomb were forced to close, but inside the yard of plant, a lot of nuclear waste had accumulated. The other tasks facing the plant are how to disassemble the contaminated power plants. The local government arranged the new system as to monitor the level of contamination, which is termed as Unit of State for Atomic System. The distance of 5km surround Krasnoyarsk 26 was set as a barrier zone. Monitoring stations are linked at 60 locations near by the plant. However, the situation and facilities are not enough to examine the level of contamination. The plant was reformed after termination of the nuclear power plant as the facilities of reprocessing of nuclear fuel waste. The plant claims that all waste materials out of Russia will be accepted for reprocessing and conservation as one of most profitable business. Until now no agreements between the local government and Krasnoyarsk 26 are made. No consensus has yet been reached by the local people. Japan and Taiwan have already sent their missions for future cooperation.
3. Usage of Isotope Batteries along the Arctic Sea coast
- The present author encountered the high radiation from the nuclear powered battery along the Arctic coast in summer 1993. Along the Arctic coast, many cargo ships transport goods between the far eastern and far western regions. In order to support the traffic, temporal light houses have been constructed on the land near by the coast. A typical light house is shown in Fig. 5. Most of the light houses are powered by Isotope batteries because in these cold and remote sites it is difficult to replace and maintain conventional chemical batteries. Inside the Isotope battery there is highly radioactive material such as 90Sr, with an intensity of 1.4 tera becquerel (360,000 curie). If one stands within 2 meters of the battery, one is exposed to high gamma radiation. If the ambient temperature is lower, the efficiency of power generation gets better. Usually this type of battery is mounted in a Satellite as a power source.
Figure 5
Typical light house along the Arctic coast, powered by Isotope battery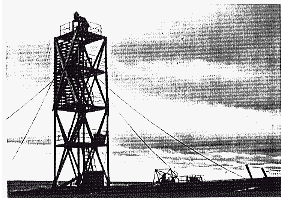
- Because of the high radiation from the battery, the special concern for its operation must be regulated by law. But in the area in remote places, these dangerous batteries are subject to no regulations. Our radioactive meter indicated the level of gamma ray is 800 times higher than the normal level.
- On some occasions, accidents have taken place due to mishandling. In 1991, near the river mouth of the Kondrashev River, one of the Isotope batteries was crashed into by a tractor. The area was highly contaminated by 90Sr. The surface of ground was scarped over 3 km2 and was dumped into the sea. Some casualties were also reported. In 1988, off Sakhalin, a navy helicopter crashed and sank into sea with an active Isotope battery. According to a source in the Russian Navy, the total number of locations, where similar types of Isotope batteries are used, is 900 or more. The security of the operation is very poor and anyone can touch, or even steal, them. No fence was constructed to prevent the accidental contact by local people. Most local people do not realize the hazardous nature of Isotope batteries.
- In some local airports in east Siberia, there exist hot spots with high radiation. For example, the airport of UST Nera reported high radiation in some spots in the airstrip. Similarly, the airport of Chokurdakh also reported high radiation. No direct evidence indicating the source of radiation was found. Local authorities had no information on this matter and even they are reluctant to open this fact to the public.
Conclusion
- Radioactive waste disposal and the related dumping of materials has caused serious contamination in Siberia. As permafrost is by its nature, non-permeable, contaminated materials are not dispersed by the surface water but accumulate in the active layer. Radioactive pollutants also accumulate in the sediments of rivers and the sea floor. Peaceful underground nuclear explosions were conducted as geophysical soundings and in the diamond industry. Harmful pollutants such as plutonium accumulate on the ground surface and tend to mix with ground water. A special task force program to evaluate the level of contamination is urgently needed. An international organization is expected to take action for the protection of further dispersion of contamination.
- The present author expresses his thanks to the people in Yakutsk, who gave him valuable information. He also expresses his thanks for Dr. G. Shaw, Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska for providing the Naval Research Report.
References
Mikulenko K. I., Tunitishin K. V. and Chomchoev A. I. (1996),"Underground Nuclear explosions and their possible effects on the arctic seaside of Yakutia", Proceedings of the First International Conference on Northern Forum in Yakutsk, p. 178.
Chomchoev A., Mikulenko K. I. and Protopopov U. (1994), "Experience
of geologic factors studying for prognosticating the radiation contamination on the territory of Sakha (Yakutia) Republic", Proceedings International Symposium Redemption and Restoration of Radioactive-contaminated sites in Europe, pp. 473-483.
Naval Research Office (1996), Arctic Nuclear Waste Assessment Program
Summary FY 1995. 570 pp. United States Defense.
- According to the report by Chomchoev et al. (1994), between 1967 and 1988, the total number of the explosions was 12. The nearest site is located at Kobyai, and is 70 km away from city of Yakutsk. On the 8th August 1978, the explosion, code named "Craton-4", was carried out at a depth of 567 m in the previously arranged bore hole. The size of the explosion was equivalent to 6.15 kt of dynamite. In that area there is a tectonic zone and a fault zone, runing from south-west to north-east. The geological setting of the Carton-4 site suggests that migration of underground water may spread out along the tectonic zone. They predicted the possible flow of contaminated water shown in Fig. 4. The most hazardous pollutant is 239plutonium, which has a half life time of about 28,000 years.